|
AG Filamentous fungi |
 |
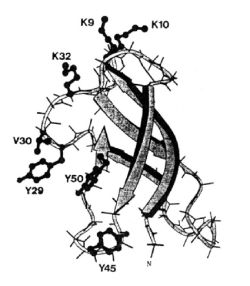
| Fig. 1: The Antifungal Protein from Aspegillus giganteus (Lacadena et al. 1995) |
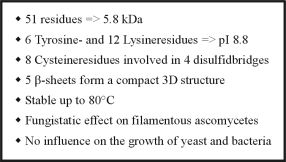 |
| Fig. 2: Features of the Antifungal Protein from Aspergillus giganteus |
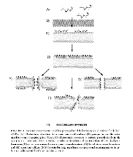 |
| Fig. 3: Proposed mode of action for antimicrobial
peptides (Tossi et al. 2000) (Click to enlarge) |
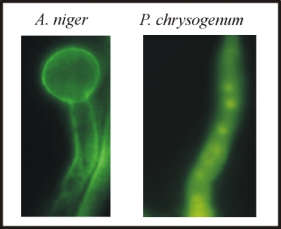 |
| Fig. 4: Localization of FITC labelled Antifungal Protein in different fungi |
| Problems? Comments? Questions? Please Contact: Webmaster Last Update: 02 / 2002 |