 Introduction Introduction
 Descriptions Descriptions
 Synonyms Synonyms
 Image Bank Image Bank
 Lecture Bank Lecture Bank
 Introduction Introduction
 Human Human
 Veterinary Veterinary
 Environmental Environmental
 Industrial Industrial
 Agricultural Agricultural
 Introduction Introduction
 Susceptibility Susceptibility
 MIC Database MIC Database
 Procedures Procedures
 Histopathology Histopathology
 Introduction Introduction
 Abbreviations Abbreviations
 Links Links
 CME CME
 Conference Conference
 Highlights Highlights
 Bibliography Bibliography
 Glossary Glossary
 Good Books Good Books
 Events Events
 Calendar Calendar
 Introduction Introduction
 Our Mission Our Mission
 Editorial Board Editorial Board
 Editorial Staff Editorial Staff
 Supporters Supporters
 Contributors Contributors
 Developers Developers
 Legal Stuff Legal Stuff
 Privacy Policy Privacy Policy
This page
updated:
1/24/2003 11:29:52 AMDoctorFungus - All Rights Reserved © 2003 Copyright
&
Privacy Policy
Site built and designed for
doctorfungus by Webillustrated |
 |
 |
 |
| You are here: Drugs
> Medical
> |
Anidulafungin (LY303366)
Anidulafungin (previously known as
LY303366 and briefly also referred to as VER-002 and
V-echinocandin) is a glucan synthesis inhibitor of the
echinocandin structural class. It is composed of the
echinocandin B nucleus with a terphenyl head group and a C5
tail. Anidulafungin has been developed by Eli Lilly
Pharmaceuticals. It has recently been licensed to Versicor for
development as a parenteral agent. It is currently in clinical
trials. Its trade name has not been announced. 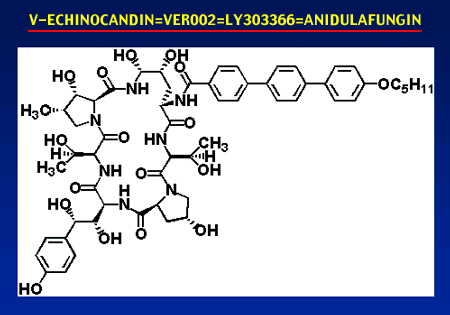
As with
other echinocandins, anidulafungin blocks the synthesis of a
major fungal cell wall component, 1-3-beta glucan, presumably
via inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase [ 1143].
Anidulafungin is active in
vitro against Candida
spp. However, anidulafungin MICs for C.
parapsilosis and C.
guilliermondii are relatively higher than those for
the other species. It has been shown to be fungicidal against
some isolates of C.
albicans and C.
glabrata [ 1609] [ 2066]. Anidulafungin does not have significant
activity against Cryptococcus
neoformans. Similarly, its activity against Blastomyces
dermatitidis, Sporothrix
schenckii, Trichosporon
beigelii, Acremonium
strictum, Rhizopus
arrhizus, Fusarium
spp. and Phialophora
spp. is limited. Anidulafungin MICs for Histoplasma
capsulatum, Cladophialophora
bantiana, Pseudallescheria
boydii, and Bipolaris
spp. are also relatively high [ 616] [ 2066]. As with caspofungin,
activity of anidulafungin against Aspergillus
spp. has been investigated by using a distinctive
parameter, "minimum effective concentration" (MEC), as well as
MIC [ 1145]. Anidulafungin MECs for Aspergillus
are in an acceptable range and lower than the MICs [ 1607] [ 1502]. For anidulafungin MICs obtained for
various types of fungi, see susceptibility
patterns and the susceptibility
database.
Typical doses for
anidulafungin are not yet known.
Results of the
clinical trials have not yet been reported.
It has oral and
intravenous formulations.
Anidulafungin is
undergoing Phase II clinical trials.
|
| 
References
616.
Espinel-Ingroff, A. 1998. Comparison of in vitro activities of the new
triazole SCH56592 and the echinocandins MK-0991 (L-743,872) and LY303366
against opportunistic filamentous and dimorphic fungi and yeasts. J Clin
Microbiol. 36:2950-2956.
1143. Kurtz, M. B., G. Abruzzo, A.
Flattery, K. Bartizal, J. A. Marrinan, W. Li, J. Milligan, K. Nollstadt,
and C. M. Douglas. 1996. Characterization of echinocandin-resistant
mutants of Candida albicans: Genetic, biochemical, and virulence studies.
Infect. Immun. 64:3244-3251.
1145. Kurtz, M. B., I. B.
Heath, J. Marrinan, S. Dreikorn, J. Onishi, and C. Douglas. 1994.
Morphological effects of lipopeptides against Aspergillus fumigatus
correlate with activities against (1,3)-b-D-glucan synthase. Antimicrob.
Agents Chemother. 38:1480-1489.
1502. Oakley, K. L., C. B.
Moore, and D. W. Denning. 1998. In vitro activity of the echinocandin
antifungal agent LY303,366 in comparison with itraconazole and
amphotericin B against Aspergillus spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
42:2726-2730.
1607. Pfaller, M. A., F. Marco, S. A. Messer,
and R. N. Jones. 1998. In vitro activity of two echinocandin derivatives,
LY303366 and MK-0991 (L-743,792), against clinical isolates of
Aspergillus, Fusarium, Rhizopus, and other filamentous fungi. Diagn.
Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 30:251-255.
1609. Pfaller, M. A., S.
A. Messer, and S. Coffman. 1997. In vitro susceptibilities of clinical
yeast isolates to a new echinocandin derivatives, LY303366, and other
antifungal agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.
41:763-766.
2066. Uzun, O., S. Kocagoz, Y. Cetinkaya, S.
Arikan, and S. Unal. 1997. In vitro activity of a new echinocandin,
LY303366, compared with those of amphotericin B and fluconazole against
clinical yeast isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.
41:1156-1157.
|

